AI in Agriculture: The Power of AI Farming
In the quiet fields and farmlands across the globe, a revolution is brewing. It’s not marked by loud protests or dramatic upheavals, but by the silent hum of machines and the soft glow of computer screens. This is the dawn of a new era AI in agriculture.
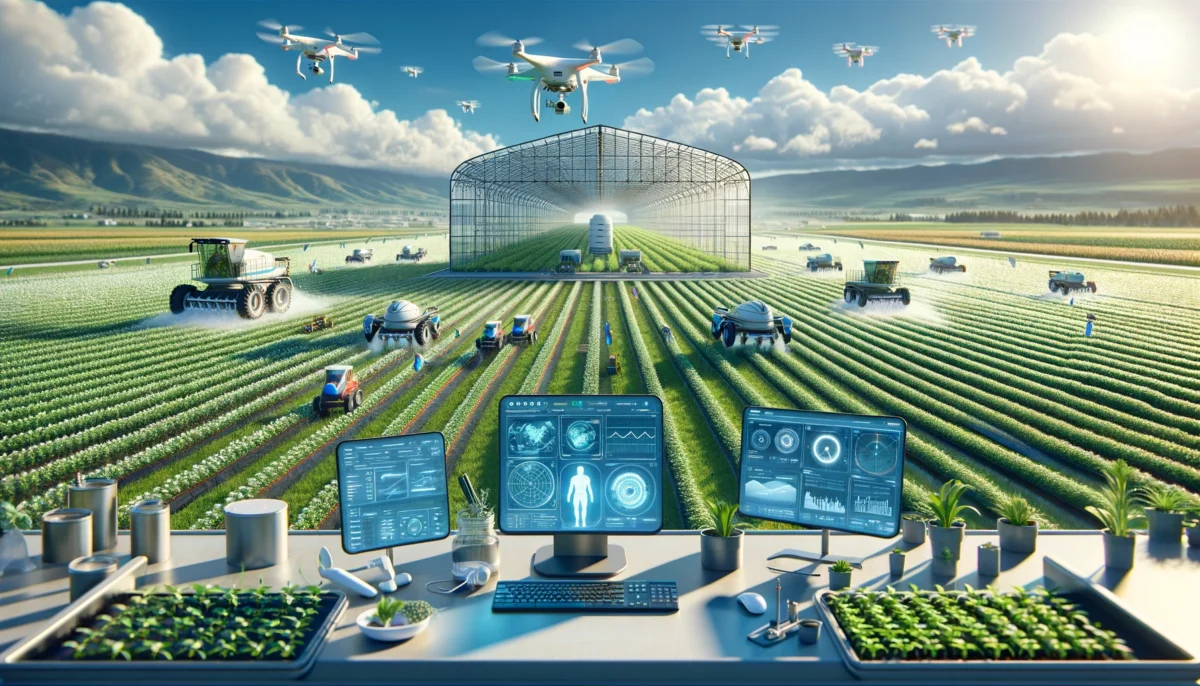

From the vast wheat fields of Kansas to the terraced rice paddies of China, AI is transforming the way we farm. It’s helping us cultivate crops more efficiently, manage resources more effectively, and combat the challenges posed by climate change.
But this is just the beginning. As we delve deeper into this article, we’ll explore how AI is not just aiding but revolutionizing agriculture, sowing the seeds for a future that’s greener, more sustainable, and bountiful. Welcome to the future of farming.
Consider reading: Future of AI in Education
What is the Role of AI in Agriculture?
AI in agriculture plays a pivotal role in optimizing farming practices and enhancing crop and livestock management. Here are key aspects highlighting the significance of AI in revolutionizing the agriculture sector:
- Precision Farming: AI enables farmers to make data-driven decisions, leading to precise resource allocation, such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides, enhancing crop yield while minimizing waste.
- Livestock Monitoring: AI tools can track individual animal health metrics, feeding patterns, and weight, enabling farmers to provide personalized care and improve overall livestock productivity.
- Disease Detection: AI algorithms can detect early signs of diseases in crops and livestock, allowing for timely intervention and preventing large-scale outbreaks, leading to improved food security.
- Pest Management: Through predictive analytics, AI can help farmers anticipate pest invasions and take proactive measures, reducing crop damage and the need for chemical pesticides.
- Labor Optimization: AI-powered machinery and robotics streamline labor-intensive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing manual workload, thereby enhancing overall productivity on farms.
- Environmental Sustainability: By optimizing resource utilization and reducing waste, AI contributes to sustainable farming practices by promoting eco-friendly approaches to agriculture.
AI’s integration with agriculture marks a significant shift towards a more efficient, sustainable, and technology-driven farming world. Its ability to analyze vast amounts of data and automate tasks is reshaping traditional farming methods, paving the way for a more productive and environmentally conscious future in agriculture.
Lifecycle of Agriculture
In the lifecycle of agriculture, climatic factors like rainfall, temperature, and humidity significantly impact farming practices. Deforestation and pollution contribute to climatic changes, making it challenging for farmers to make decisions on soil preparation, seed sowing, and harvesting.
- Every crop requires specific nutrients in the soil, with nitrogen (N), phosphorous (P), and potassium (K) being the key elements needed for optimal crop growth.
- Nutrient deficiencies can lead to poor-quality crops, affecting yield and quality.
- Weed protection is crucial in agriculture, as uncontrolled weed growth can increase production costs and deplete soil nutrients.
Innovative technology, such as NLP software and drones, plays a pivotal role in modern precision agriculture by optimizing resource allocation, reducing chemical usage, and enhancing crop management practices.
The integration of AI solutions in agriculture optimizes farming processes, improving efficiency, sustainability, and overall productivity in the agricultural sector.
Challenges faced by farmers by using traditional methods of farming
Farming practices have evolved significantly with the advent of AI in agriculture, but many farmers still rely on traditional methods. These methods come with their own set of challenges that hinder efficiency and productivity in today’s agricultural world:
- Limited Precision: Traditional farming techniques lack the precision and accuracy provided by modern AI technologies. This leads to challenges in targeted weed control and pesticide application, resulting in decreased crop yields.
- Resource Inefficiency: Without the use of AI-driven analytics, farmers often struggle with resource optimization. This inefficiency can lead to overuse of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, impacting both the environment and the farmer’s bottom line.
- Manual Labor Dependence: Traditional farming methods often require extensive manual labor, leading to increased labor costs and potential health risks for farmworkers. This reliance on manpower can limit the scalability and sustainability of farming operations.
- Risk of Crop Failure: Inaccurate weather forecasting and pest/disease management pose significant risks to crops when traditional methods are used. Without real-time data analytics and predictive modeling, farmers are more susceptible to unforeseen crop losses.
- Yield Variability: Traditional farming practices may struggle to address variations in soil quality and nutrient levels across different areas of a farm. This can result in inconsistent crop yields and overall productivity.
Addressing these challenges requires a shift towards embracing AI technologies in agriculture. By adopting innovative solutions, farmers can overcome these obstacles and pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in farming practices.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture
- Irrigation Optimization: AI technology helps in precise irrigation by analyzing data from sensors to determine crop water needs accurately.
- Pest Management: Combining drone data and ground sensors, AI can predict and prevent pest infestations, reducing crop losses.
- Weed Control: AI-powered systems can identify and target weeds specifically, minimizing the use of herbicides and reducing environmental impact.
- Spraying Efficiency: AI enables customized pesticide application based on real-time data, optimizing spraying patterns to minimize waste.
- Labor Efficiency: Automation through AI in agriculture reduces manual labor dependence, making farming practices more efficient and cost-effective.
- Yield Prediction: AI algorithms analyze various factors like weather patterns and soil conditions to forecast crop yields accurately.
- Resource Management: By monitoring plant health levels and nutrient requirements, AI helps in efficient resource allocation for optimal crop growth.
| Data Point | Value |
|---|---|
| Increase in Crop Yield with AI Technology | 20-30% |
| Reduction in Herbicide Usage | Up to 90% |
| Efficiency in Water Usage | Up to 50% |
Consider reading: How Chat GPT Can Significantly Increase Productivity
Final Thoughts on AI in Agriculture
In wrapping up, AI is revolutionizing agriculture by boosting crop yields, minimizing herbicide use, and optimizing water efficiency. By harnessing AI technologies, farmers can streamline operations, decrease manual labor, and promote sustainable farming practices.
The future of agriculture lies in the seamless integration of AI solutions to address challenges and enhance productivity. As we continue to embrace AI advancements, the agricultural sector will witness unprecedented growth, ensuring food security and environmental conservation for generations to come.
FAQs on AI in Agriculture
How is AI being used in agriculture?
In agriculture, AI is used to enhance farming decisions by processing sensor and satellite data to track soil moisture, weather, and crop health. This advanced analysis leads to maximized crop yields, efficient resource use, and effective management of farm operations.
What are the 3 most popular applications of AI in agriculture?
The three most popular applications of AI in agriculture are precision farming, agricultural robots, and predictive analytics. Precision farming utilizes AI to optimize field-level management, agricultural robots automate tasks such as harvesting and weeding, while predictive analytics help forecast weather and assess crop health for better decision-making.
Which country uses AI in agriculture?
Brazil is leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) in its agriculture sector, employing advanced technologies to enhance crop monitoring, resource management, and yield prediction, as well as for pest and disease control through AgTech companies like Strider.
What are the three ways AI can help farmers tackle the challenges of modern agriculture?
AI can significantly aid farmers in facing modern agricultural challenges through three innovative approaches: by implementing federated learning for collaborative data analysis, employing advanced algorithms for precise pest and disease detection, and utilizing predictive analytics to forecast crop prices more accurately. These AI applications enhance decision-making and improve farm efficiency.